Vernier Acuity Test
Vernier acuity refers to the minimum angular separation required to detect that two lines placed end to end are not co-linear. The human visual system is remarkably good at performing this task and trained observers can resolve displacements of less than 10 seconds of arc. Vernier acuity has been shown to be remarkably immune to image degradation – in other words, blurring or distorting the image does not greatly affect measurements.
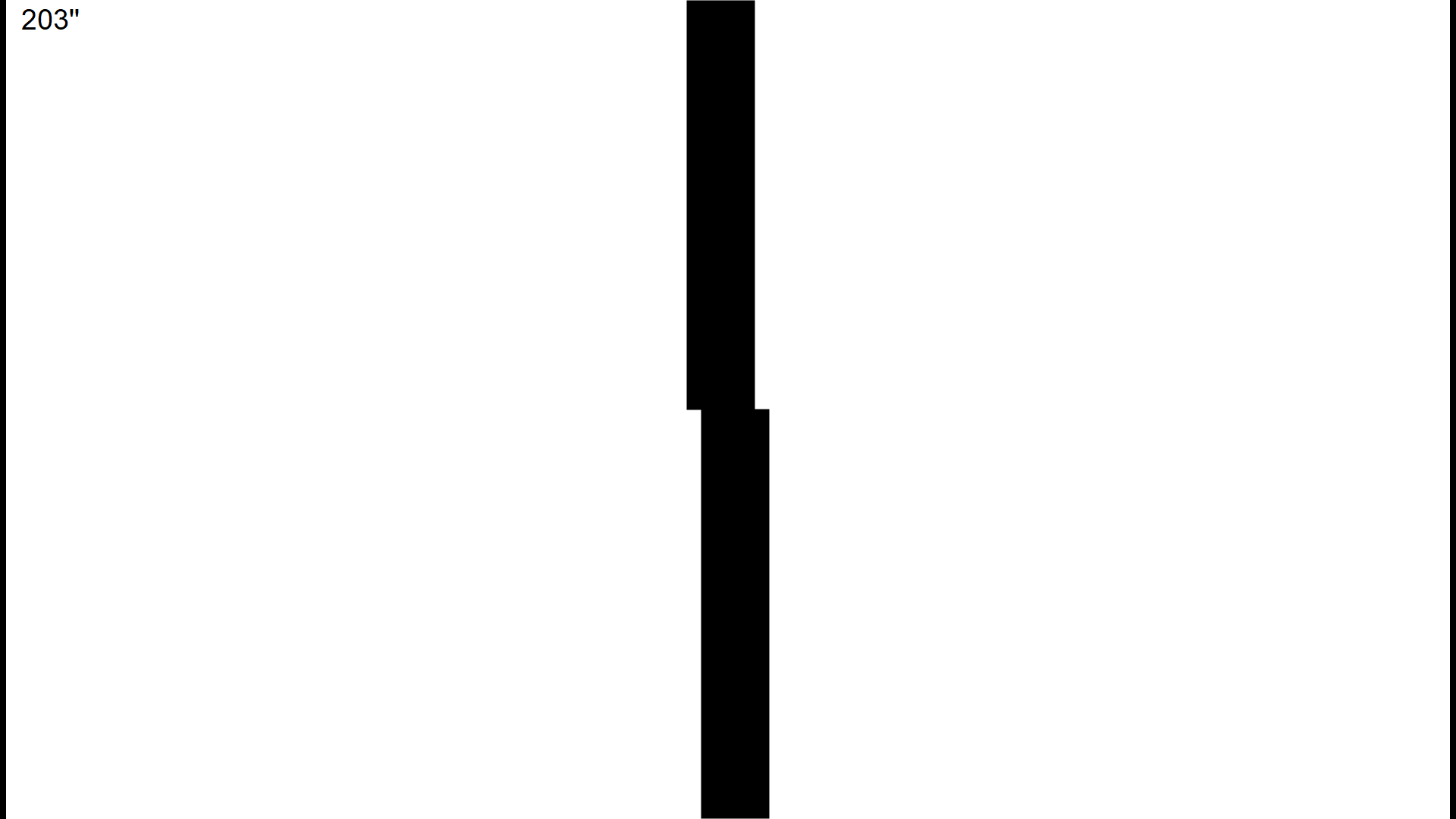
The clinical value of this is that it provides an assessment of macula function for people who have poor quality optics. For example, patients with cataracts may still achieve good vernier acuity even when their normal visual acuity is reduced. This allows the clinician to assess the integrity of the macula in these patients, which is particularly useful when it is not possible to get a clear view of the fundus.
When the Vernier Acuity test is selected, the following options are available:
Mouse The separation of the bars may be changed using the scroll bar on the Secondary toolbar. The current separation is shown on the test information bar Select R to toggle a label on and off on the screen, giving the current separation of the bars |
|
Keyboard Use the vertical cursor control keys to change the separation of the bars R to toggle a label on and off on the screen, giving the current separation of the bars |
|
|
Remote Use the vertical arrows to change the separation of the bars R to toggle a label on and off on the screen,giving the current separation of the bars |
